Novel research led by Wei Qin, an assistant professor of microbiology at the University of Oklahoma, that significantly changes the understanding of ammonia oxidation, a critical component of the global nitrogen cycle, has been published in the journal Nature Microbiology.
Ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms, commonly called AOM, use ammonia for energy and account for the annual oxidation of approximately 2.3 trillion kilograms of nitrogen in soil, freshwater, the subsurface, and human-made ecosystems. One major question that has remained unanswered for decades is how different lineages of AOM species coexist in the same environment: do they compete for ammonia or instead use other alternative compounds for their energy needs?
“The different lineages of AOM are simultaneously growing in the same environment and were thought to primarily compete for ammonia,” Qin said. “Our collaborative research focused on determining why and how these metabolically conserved lineages are able to coexist without direct competition for inorganic nitrogen (ammonia), and we examined their abilities to use organic nitrogen (urea) instead.”
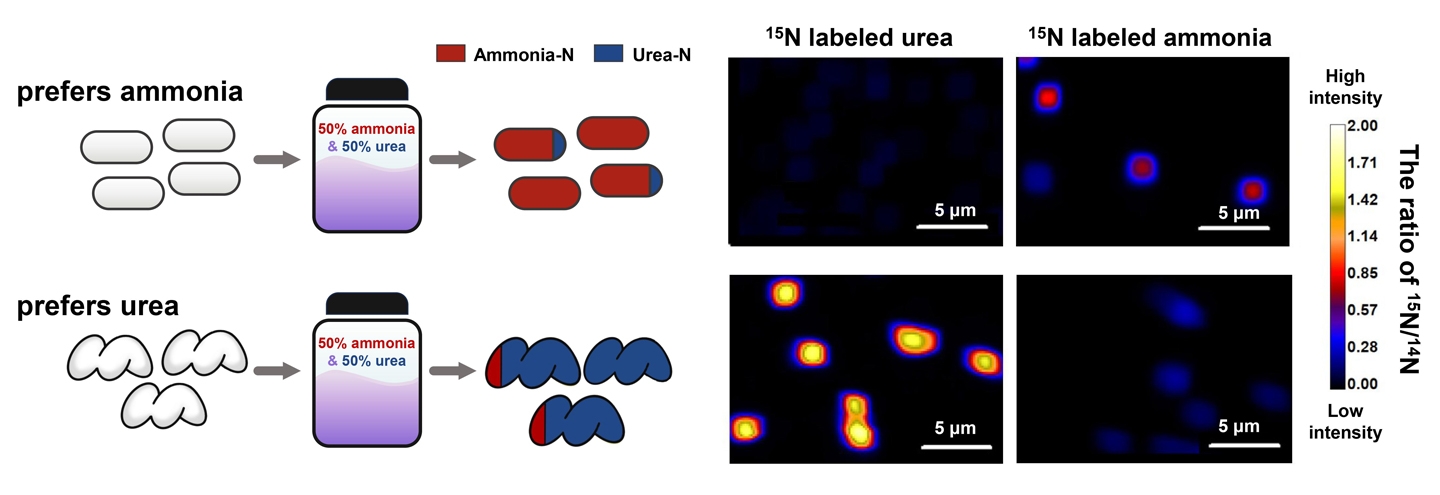
More than half of the AOM species have adapted to utilize urea, a widely available organic nitrogen compound that accounts for approximately 40 percent of all nitrogen in fertilizers, as an alternative energy source. This process, however, requires AOM to use an additional energy because urea is a more complex molecular structure and needs to first be broken down into ammonia inside the AOM cells before further utilization. Knowing this, Qin’s collaborative team sought to understand how AOM acquire and metabolize ammonia and urea when both are available simultaneously.
“We always called urea an alternative substrate to ammonia,” Qin said. “Now, we realize that a major lineage of AOM actually prefer urea and repress the use of ammonia when urea is present. This discovery challenges dominant assumptions that had persisted for more than 100 years since the cultivation of the first AOM species.”
The research findings show that different AOM lineages employ different regulatory strategies for ammonia or urea utilization, thereby minimizing direct competition with one another and allowing for coexistence. These differential preferences reveal a hidden physiological biodiversity and have real-world consequences that will need to be explored further.
“The AOM produce either nitrate, which leaches into groundwater and surrounding bodies of water, causing eutrophication, or nitrous oxide, which is a powerful greenhouse gas.” Qin said. “Once we confirm which AOM lineages prefer urea, we could investigate their contribution to nitrate leaching and greenhouse gas production in the environment. This is necessary for developing sustainable and practical approaches to reducing these nitrogen pollutants in natural and engineered ecosystems. This will likely be the focus of future research.”
Read more about this research in the article, “Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea exhibit differential nitrogen source preferences," in the journal Nature Microbiology. DOI no. 10.1038/s41564-023-01593-7 and learn more about Qin’s research with the Qin Lab.
This project represents the collaborative effort of 13 authors from the School of Biological Sciences and Institute for Environmental Genomics at the University of Oklahoma, alongside authors from the University of Washington, University of Florida, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Princeton University, Xiamen University and Nanjing Agricultural University. This work was supported by grants from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science, Division of Biological and Environmental Research, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, the Department of Agriculture National Institute of Food and Agriculture, Simons Foundation, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and others.