Module 6 Instructional Analysis for DL
Section 3: Content Analysis for Distance Learning Program
In analyzing learning content for a distance learning program, four methods of content analysis are used.
- Task analysis
- Critical incident analysis
- Topic analysis
- Mind mapping
Task Analysis
Task analysis is one of the most commonly used methods to analyze instructional content. Task analysis analyses what a learner is required to do in terms of actions and/or cognitive processes to achieve a task. Task analysis makes it possible to design and allocate tasks appropriately within a working environment. The functions need to be included within the task situation so that the user interface can then be accurately specified.
Typical procedure of task analysis follows (Crystal & Ellington, 2004):
- Identify the task to be analyzed.
- Break this down into between 4 and 8 subtasks. These subtasks should be specified in terms of objectives.
- Decide upon the level of detail into which to decompose. Making a conscious decision at this stage will ensure that all the subtask decompositions are treated consistently. It may be decided that the decomposition should continue until flows are more easily represented as a task flow diagram.
- Present the analysis to someone else who has not been involved in the decomposition but who knows the tasks well enough to check for consistency.
Task Order
In conducting task analysis tasks and subtasks should be ordered based on the following criteria.
- Job-task order: according to the procedures and steps of the task
- Simple-to-complex order: concepts and overall skills
- Psychological order: grouping by related content (rules and principles)
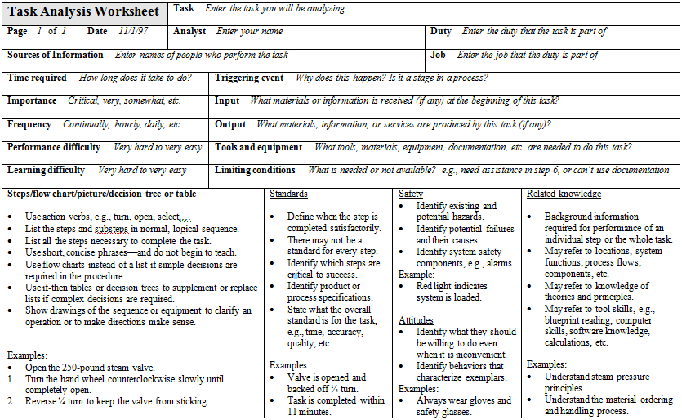
An Example Task Analysis Sheet
*Click above image to see the full image.More Illustration about Task Analysis
Critical Incident Analysis
According to Wikipedia, critical incident method is a set of procedures used for collecting direct observations of human behavior that have critical significance and meet methodically defined criteria. These observations are then kept track of as incidents, which are then used to develop broad psychological principles and learning content for behavioral correction. A critical incident can be described as one that makes a significant contribution - either positively or negatively - to an activity or phenomenon. Clinical incidents can be gathered in various ways, but typically the following procedure is adopted:
1. Determine the critical tasks based on:
- Frequency of the task performance
- The severity of the consequence for failure to perform the task
- Restrictions to be performed by certain people2. Determine important but nonessential tasks.
- Are performed occasionally?
- Constitute background?
- Provide supporting knowledge not directly related to job tasks?3. Determine the tasks you will deselect as they are:
- Rarely performed
- Not critical to job performance
- Easily learned
- Prerequisite skill for employmentAdvantages of Critical Incident Method
- Information is collected from the respondent's perspective and in his or her own words.
- Does not force the respondents into any given framework.
- Identifies even rare events that might be missed by other methods which only focus on common and everyday events.
- Useful when problems occur but the cause and severity are not known.
- Emphasizes the features that will make a work situation particularly vulnerable and can bring major benefits (e.g. safety).
Disadvantages of Critical Incident Method
- Since critical incidents often rely on memory, incidents may be imprecise or may even go unreported.
- Possibility of the built-in bias towards incidents that happened recently may be exist.
- It will emphasize only rare events; more common events will be missed.
More Illustration about Critical Incident Method
Topic Analysis
Topic analysis is another commonly used method to develop content areas to be taught for a distance learning program. In analyzing learning content, the following procedure is utilized.
Procedure
- Ask a subject matter expert (SME) to describe the major categories to explain the topic.
- Ask the SME to further define each of these categories.
- The SME provides detailed information on each category.
- Once finished the analysis up to the third step, organize the content with the following steps:
- Review the analysis and identify the different content structures.
- Group related facts, principles, interpersonal skills and attitudes.
- Arrange the various components into a logical and sequential order.
- Prepare the final outline to represent the content analysis.
Topic Content Structure
- Facts
- Concepts
- Principles or rules
- Procedures
- Interpersonal skills
- Attitudes
More Illustration about Topic Analysis:
https://edtechbooks.org/id/task_and_content_analysis
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is another creative way to analyze learning content for distance learning. Below steps are a typical procedure to conduct the mind mapping method.
Procedure
- Brainstorm a list of the ideas for an instruction. (concept, process, system, etc.)
- Choose the central idea and write one or two sentences that encapsulate the idea.
- Relate the central idea to other ideas. (Concept mapping).
- Organize the central and supporting ideas in a logical order.
- Develop lessons for the main and supporting ideas.
Examples of Instructional Content from Mind Mapping
- Facts (single pieces of information)
- Concepts (ideas or definitions)
- Processes (systems of related ideas)
- Procedures (steps within a process)
- Principles (rules and guidelines)
- Systems (physical entities with operational parts)
More Illustration about Mind Mapping
Learning Activity 2 I believe you have now selected the topic of your individual project developing a learning module for a distance learning program. In order to move to the next step, what content analysis method would you use to identify the required learning content of your learning module? Provide the title of learning module, target learners, and your selected content analysis method for your individual project along with your rationale to choose the method.
Submit your answer in the discussion forum (Forum-Module 6, Topic-Content Analysis) under the Discussions area of the class homepage. Also review three other students threads and reply them with appropriate suggestions for each student's analysis. (2 points)

Previous